Scaling Machine Learning
10 February 2025
An excerpt from an article written by Sree, published in ‘Generative AI’ Journal.
Machine learning is transforming businesses in ways we never thought possible, especially in marketing and consumer analytics. It’s all about using data-driven insights and predictions to make smarter decisions. But here’s the thing - while many of us learn the basics of ML from courses and tutorials, they rarely cover the practical side, like setting up Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. And honestly, those pipelines are what make it possible to scale ML models and solve real-world problems.
In this blog, I’ll explain what CI/CD pipelines are using a simple analogy: building and delivering cars. Just like an assembly line makes car production smooth and efficient, CI/CD pipelines help streamline the process of creating and deploying machine learning models. I hope this serves as a practical, beginner-friendly guide to CI/CD pipelines in machine learning workflows for data scientists, analysts, and anyone curious about the topic.
What Is a CI/CD Pipeline and why does it matter?
Let’s start with the basics: what is a CI/CD pipeline?
At its core, a CI/CD pipeline is a set of automated processes that help you build, test, and deploy machine learning models efficiently.
Imagine you’re building a car on an assembly line. Every step - from sourcing raw materials, assembling parts, testing the vehicle, to rolling it off the line - is carefully automated to ensure everything works as it should. CI/CD pipelines do the same for machine learning projects:
a) CI (Continuous Integration): This is like assembling the car’s parts in the factory. Each time you add a new part (or code change), it’s tested to make sure everything fits and works together seamlessly.
b) CD (Continuous Deployment): Think of this as delivering the finished car to the dealership. It ensures your model is automatically deployed into production without any hiccups, ready to deliver value.
In simpler terms, CI/CD pipelines are like an assembly line for your ML projects. They take care of the repetitive tasks so you can focus on what really matters - creating impact.
Why does understanding and implementing CI/CD pipelines matter? It helps you:
a) Scale your machine learning models.
b) Solve tough business problems faster and more effectively.
c) Deliver real value to your team and stakeholders with smarter, data-driven solutions.
Honestly, these are the kind of lessons I wish someone had shared with me earlier in my career. And I hope this walkthrough gives you a clear and practical understanding of how to build and scale ML systems effectively on the cloud.
A Three-Pipeline Framework for CI/CD in Machine Learning
When it comes to real-world projects, a solid CI/CD setup needs three key pipelines working together seamlessly
a) Initial Training Pipeline: The starting point where models are built and trained using historical data.
b) Prediction Pipeline: The engine that powers batch or real-time predictions to generate actionable insights.
c) Re-training Pipeline: Keeps your models fresh by updating them as new data or changes come in.
Let’s take a closer look at each pipeline to see how they all work together in the ML lifecycle!
1. Initial Training Pipeline
This is where every ML project kicks off. It’s all about taking a model from an idea to something ready for action. Here’s how it works:
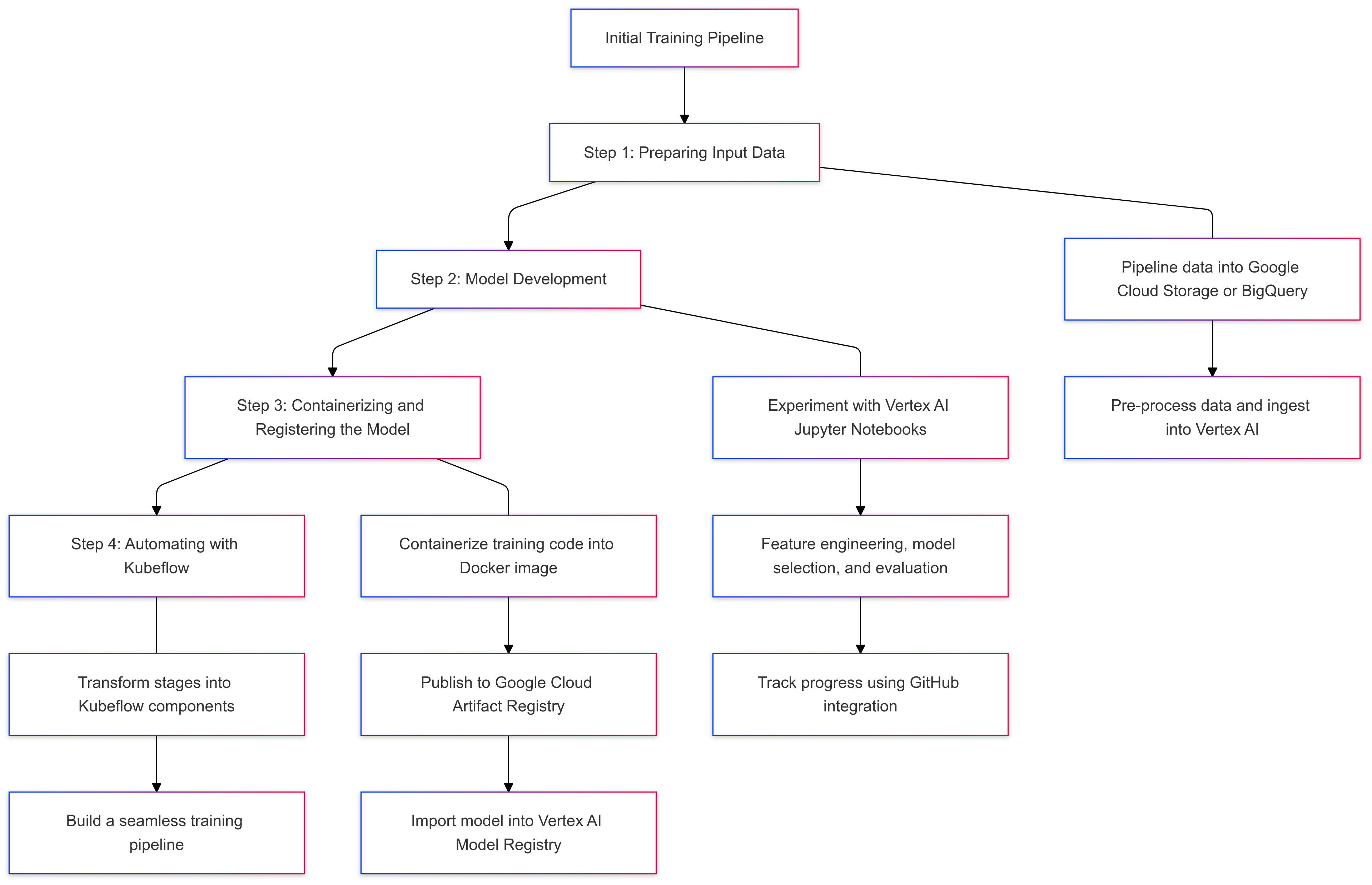
Step 1.1: Getting Your Data Ready
Think of this step as gathering the ingredients to build a car. You need all the parts - wheels, steel, an engine - before you can even think about assembly. For machine learning, it’s the same: you need to collect and prepare your input data first.
At my workplace, we use Google Cloud for this, relying on tools like Google Cloud Storage Buckets, BigQuery tables, and Vertex AI Jupyter Notebooks to handle everything. Depending on your setup, your raw data will live in something like Cloud Storage or BigQuery. Once you’ve got your data, the next step is to clean and process it - just like polishing car parts and making sure everything’s in the right shape for assembly. Then it’s ready for the real machine learning work in Vertex AI.
This step might take time and expertise, but it’s the foundation for everything else in your pipeline. Get it right, and you’re setting yourself up for success.
Step 1.2: Experimenting and Building the Model
Now that you’ve got all the parts ready, it’s time to start assembling the car. This is where the real work happens - you experiment, test, and refine until everything comes together perfectly.
In machine learning, this is all about figuring out what works. I use Vertex AI’s Jupyter Notebooks to load the cleaned data and try different tools like PyTorch, Scikit-learn, or TensorFlow. Here’s how it usually goes:
a) Feature Engineering: This step focuses on extracting meaningful patterns from the data; like designing each car part to ensure it works well.
b) Testing Models: Similar to testing car prototypes, you experiment with different models and fine-tune them to find the best performer.
The great thing about Vertex AI notebooks is how smoothly they integrate with GitHub. You can track everything - your code, parameters, and results - so nothing gets lost along the way. It’s like having a detailed log of every tweak and test you’ve done, making the process organized and efficient (Please Note: Depending on your setup, you might use other cloud-based tools like Amazon SageMaker or Azure ML Notebooks instead. They are all on par.)
Step 1.3: Packaging and Registering the Model
After your car (or model) is built, the next step is to get it ready for delivery so it can perform anywhere it’s needed. Imagine shipping a car from a factory to dealerships around the world. Whether it’s going from Thailand to Sydney or China to California, the goal is the same - when it arrives, it’s in perfect condition and ready to hit the road. That’s exactly what we aim for with your machine learning model.
Here’s how it works:
a) Containerization: Think of this as putting the car into a secure shipping container. Your model is packed into a Docker image, making it portable and ready to go anywhere.
b) Publishing: Once it’s packed, the model is “shipped” by uploading it to Google Cloud Artifact Registry. This makes it versioned and easy to access when needed.
c) Registration: Finally, just like registering a car before it hits the road, your model is added to Vertex AI’s Model Registry. This keeps track of all your versions and ensures smooth deployment.
With these steps done, your model is ready to “hit the road” and perform wherever it’s needed!
Step 1.4: Automating the Process
Once your model is packaged, shipped, and registered - just like a car arriving at its destination - it’s time to make the whole process more efficient. Imagine if you had to manually handle every step for each car: loading it into the container, tracking the ship, unloading it at the port, and registering it. That would take forever, right?
This is where automation comes in. Instead of doing the same steps over and over, you streamline the process to save time and effort.
Here’s how it works:
a) Break down your training pipeline - steps like data prep, model training, and deployment - into smaller pieces. Each component handles a specific task, like tools on an assembly line.
b) Connect these components into one seamless, automated pipeline that takes care of everything from start to finish.
With this setup, you can focus on building and improving your models while letting the pipeline handle all the repetitive, behind-the-scenes work!
Step 2: Prediction Pipeline
Once your model is trained, it’s time to put it to work - just like a car hitting the road after all the manufacturing is done. The prediction pipeline is where your model starts turning raw data into useful insights, whether through batch processing or real-time predictions.
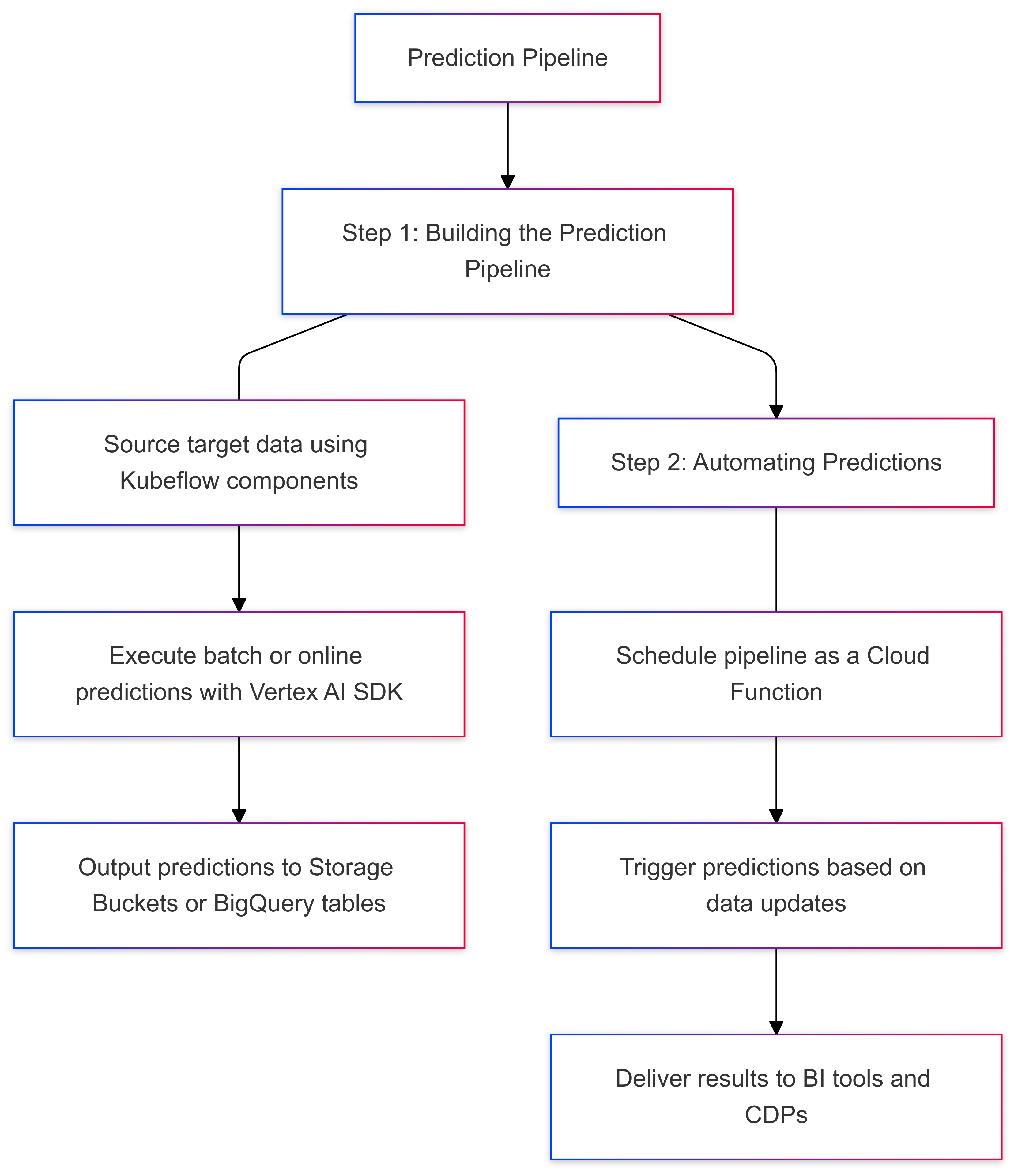
How Predictions Are Automated
Here’s how it works:
a) First, the pipeline pulls the target data from Google Cloud Storage Buckets - think of this as fueling up the car.
b) Next, the model processes the data and saves the predictions back into storage buckets - just like the car delivering goods to their destination.
To make things even easier, you can automate this process with a Cloud Function. For example, if your business needs daily predictions, you can set it up so the pipeline automatically runs whenever new data arrives - like scheduling your car for daily deliveries or school drop-offs.
How Businesses Use These Predictions
These predictions can drive all kinds of business decisions, such as:
a) Creating data visualizations with BI tools to uncover trends.
b) Launching personalized marketing campaigns through email, SMS, or web notifications.
c) Running targeted ads across platforms like video, display, or search.
It’s all about turning your data into action, just like putting your car to work after all the preparation!
3. Re-training Pipeline
No car stays in top condition forever - roads change, wear and tear happens, and maintenance is essential to keep it running smoothly. The same applies to machine learning models. No model stays perfect forever - data changes, patterns evolve, and models need updates to stay accurate. That’s where the re-training pipeline comes in. It helps your ML systems keep up with the times and deliver their best performance, just like a car that gets regular servicing.
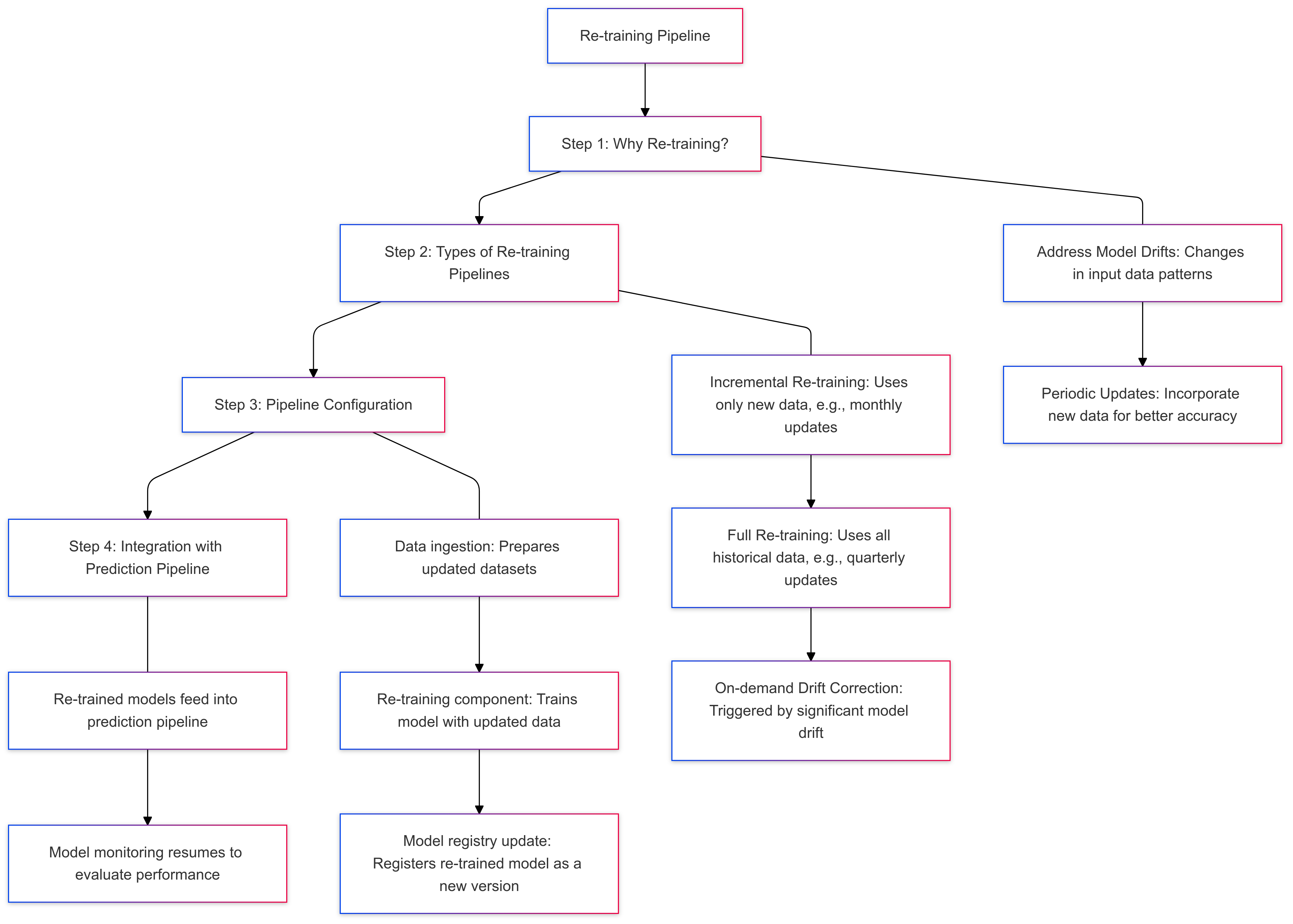
Types of Re-training Pipelines
There are three main ways to re-train your model, depending on what’s needed:
a) Incremental Re-training: This adds new data to the model to keep it up to date, like topping off the oil or adding fuel to a car. It’s great for regular updates, like monthly refreshes.
b) Full Re-training: This starts from scratch, using all your data for a fresh rebuild. Think of it as overhauling the car’s engine - usually done less often, like quarterly updates.
c) Drift Correction: This kicks in when something goes wrong, like a car repair after an unexpected breakdown. It’s used to fix a drop in the model’s performance.
How the Pipeline Works
Every re-training pipeline has three main steps:
a) Data Prep: This is where you get the updated dataset ready for training - like gathering the tools and parts needed to service a car.
b) Re-training: Think of this as servicing the model. It could be a quick update or a complete rebuild, depending on what’s needed.
c) Model Registry: Just like keeping a car’s maintenance records, the updated model is saved in the registry to track its latest version.
Once the re-trained model is ready, it connects back to the prediction pipeline. This creates a smooth, ongoing cycle where the model keeps improving and stays in sync with new data over time.
Wrapping Up
For data scientists, analysts, or BI professionals, understanding how to build and manage these pipelines can be a game-changer. It’s not just about theory - these skills help you create scalable ML systems that really make an impact.
I hope this gives you a simple and practical look at how CI/CD pipelines work, especially in marketing and analytics. In future posts, I’ll dive deeper and show you how to build a complete, end-to-end pipeline using open-source datasets. These lessons have been invaluable in my career, and I hope they’ll help you too!
About the Author
Sree is a Marketing Data Scientist and seasoned writer with over a decade of experience in data science and analytics, focusing on marketing and consumer analytics. Based in Australia, Sree is passionate about simplifying complex topics for a broad audience. His articles have appeared in esteemed outlets such as Towards Data Science, Generative AI, The Startup, and AI Advanced Journals. Learn more about his journey and work on his portfolio - his digital home.